Real-Life Applications of Circles (Conic Sections)
Wheels and Gears: The most common real-life example of a circle is a wheel. The design of wheels, gears, and bearings in mechanical engineering relies on the properties of circles.

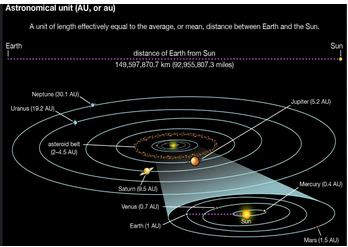
Astronomy: While orbits are elliptical, many celestial bodies such as moons or planets often follow nearly circular orbits around a star. Additionally, the circular shape is fundamental in satellite dish design, where a parabolic dish reflects signals to a focal point.
Architecture and Engineering: Arches, domes, and circular columns are all structural elements in architecture that rely on the geometry of circles.

Optics: In optics, mirrors and lenses often have circular shapes, such as in telescopes, where the curvature of the mirror or lens helps focus light to a single point.

Art and Design: Circles are frequently used in design, from logos to architecture, for aesthetic symmetry and harmony.