Properties of a Circle
A circle has several important parts, each with its own definition and properties. Understanding these parts is crucial for solving problems related to circles and for applying circle concepts in real-life situations.
Parts of a Circle
Center: The fixed point from which all points on the circle are equidistant. It is usually denoted by the letter O.

Radius: The distance from the center of the circle to any point on the circle. It is denoted by r. All radii of a circle are equal.

Diameter: A chord that passes through the center of the circle. It is the longest chord of the circle and is twice the length of the radius. It is denoted by d.

Circumference: The distance around the circle. It is the perimeter of the circle and is given by the formula:

C = 2πr
Chord: A line segment with both endpoints on the circle. A diameter is a special type of chord.


Arc: A part of the circumference of the circle. An arc can be a minor arc (less than 180 degrees) or a major arc (more than 180 degrees).

Sector: A region bounded by two radii and the arc between them. It resembles a "slice of pie."

Segment: A region bounded by a chord and the arc between the chord's endpoints. It is different from a sector.

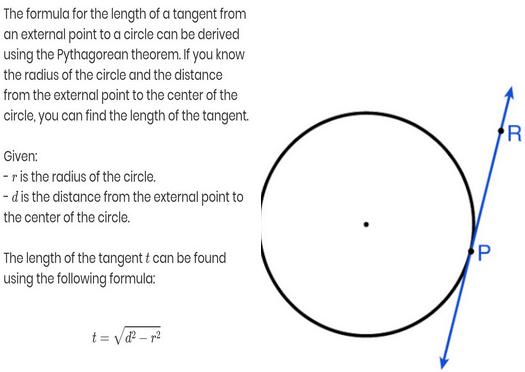
Tangent: A line that touches the circle at exactly one point. This point is called the point of tangency. A tangent is perpendicular to the radius at the point of tangency.

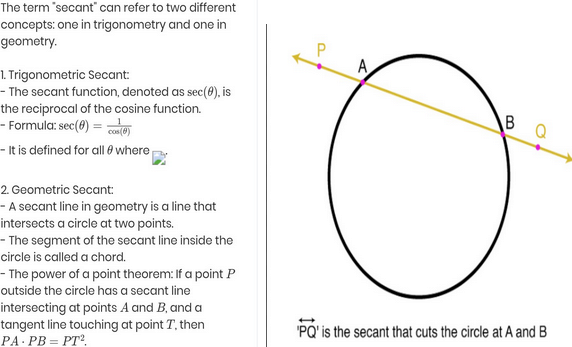
Secant: A line that intersects the circle at two points. It extends beyond the circle, unlike a chord which is confined within the circle.
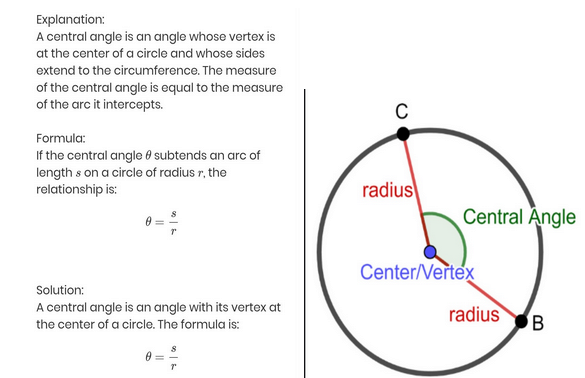
Central Angle: An angle whose vertex is at the center of the circle and whose sides are radii. The measure of a central angle is equal to the measure of the arc it intercepts.
Inscribed Angle: An angle formed by two chords in a circle which have a common endpoint. The vertex of the inscribed angle lies on the circle, and its measure is half the measure of the intercepted arc.

For Further Understanding
Here are some additional videos about the parts of a circle.
Summary
To summarize, the key parts of a circle include the center, radius, diameter, circumference, chord, arc, sector, segment, tangent, secant, central angle, and inscribed angle. Each part has specific properties and plays a role in various geometric and real-life applications. Understanding these parts is essential for solving problems related to circles and for applying circle concepts in different contexts.